Small Body Science Simulation
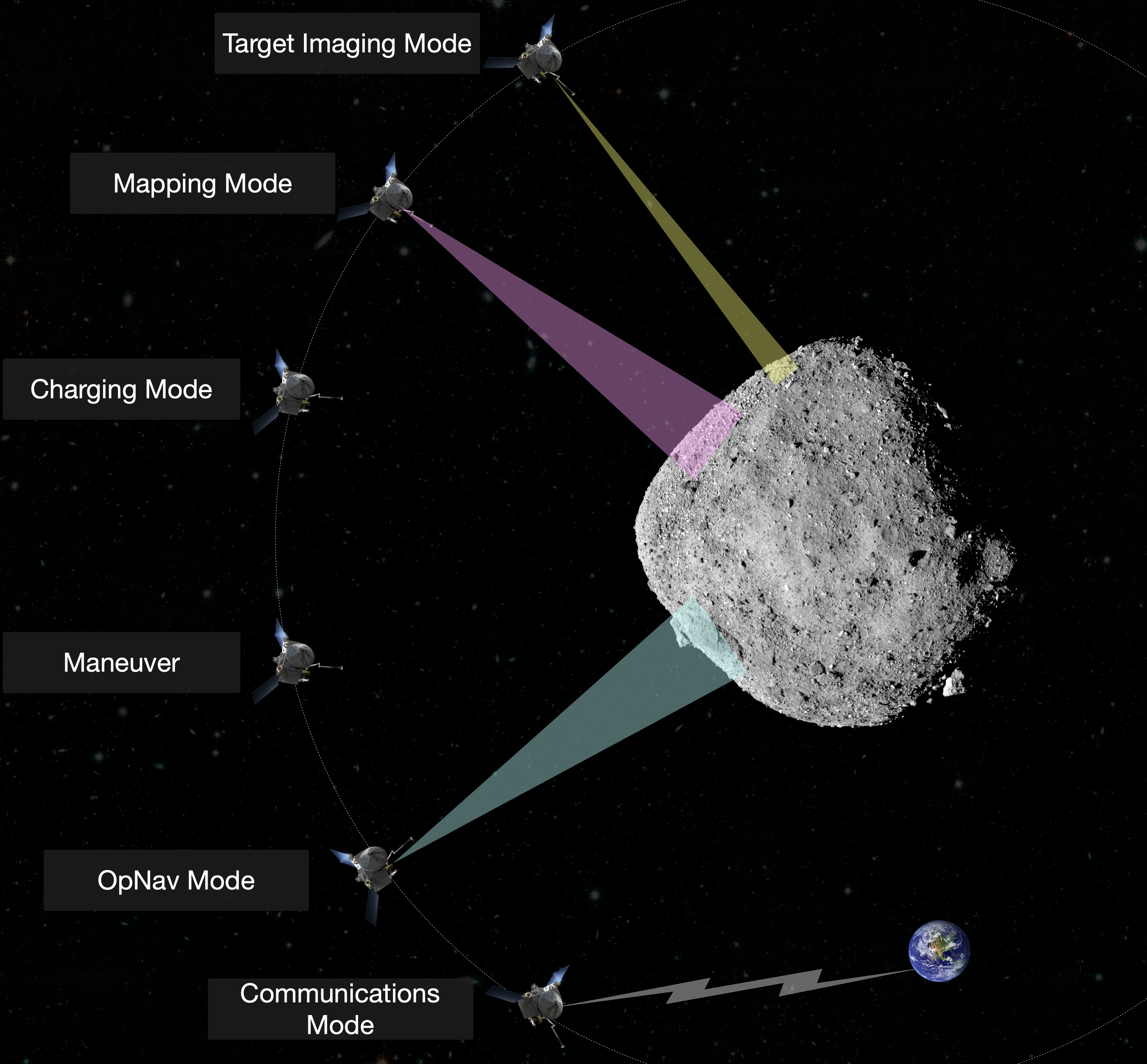
This is a simulator created for reinforcement learning research that utilizes the Basilisk astrodynamics software architecture. In the small body science operations problem, a spacecraft moves between waypoints defined in the small body’s Hill frame while collecting mapping data and surface target images. The spacecraft has access to the DSN every 24 hours and has to manage resources such as battery charge, data buffer storage, and fuel while avoiding collision with the body. The spacecraft is collecting three separate spectroscopy maps, each at a specific solar phase angle. The spacecraft also has a set of 10 surface targets that represent candidate landing sites it is attempting to image.